Dialectical Behavior Therapy Center in Washington State
The inability to control or regulate one’s emotions is often one of the primary reasons someone ends up dealing with substance abuse and addiction. A dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) program gives those recovering from substance abuse a set of reliable practices to help them manage their emotions, end their dependency, and minimize the risk of relapse.
DBT is an evidence-based therapy practice that helps individuals create meaningful connections which can substantially improve the quality of their lives and, most importantly, help them achieve their goals of sobriety.
Therapists use DBT with patients to help them control and respond to negative emotions, behaviors, and social interactions such as destructiveness, impulsiveness, and disconnection before they continue substance use or relapse.
Often, individuals may respond to these negative impulses by self-medicating, which only creates additional problems for the user to overcome.
However, once an individual learns how to control their emotions by practicing these techniques, they are much less likely to require drugs and alcohol to self-regulate themselves and feel good.


Who Can Benefit
from Dialectical Behavioral Therapy?
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) is a versatile and effective treatment approach that can benefit a wide range of individuals. Initially developed to treat borderline personality disorder (BPD), DBT has since been adapted and proven effective for various mental health and behavioral issues. Some of the people who can benefit from DBT include those struggling with:
DBT was specifically designed to help individuals with BPD manage intense emotions, improve interpersonal relationships, and reduce self-destructive behaviors.
DBT can be an effective tool in addiction treatment, as it helps individuals develop coping skills, manage cravings, and address the underlying emotional and psychological issues contributing to substance abuse.
DBT has been shown to be helpful for individuals dealing with eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder by teaching healthy coping mechanisms and addressing emotional dysregulation.
Individuals experiencing depression or anxiety disorders can benefit from DBT’s focus on emotional regulation, mindfulness, and distress tolerance, which can help them manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
DBT can help individuals with PTSD process traumatic experiences, manage emotional triggers, and develop healthier coping strategies.
As DBT emphasizes emotional regulation and distress tolerance, it can be beneficial for individuals who struggle with suicidal thoughts or engage in self-harming behaviors.
DBT can assist individuals with bipolar disorder in managing mood swings, improving interpersonal relationships, and developing healthy coping strategies.
DBT can help individuals with ADHD to improve impulse control, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness.
For those dealing with multiple mental health issues or a combination of mental health and substance use disorders, DBT can provide a comprehensive approach to address the complex needs of these individuals.
It is essential to note that while DBT can be beneficial for many people, the specific treatment plan should be tailored to the individual’s unique needs and circumstances. If you or someone you know is struggling with any of the above issues, it is crucial to consult with a mental health professional to determine if DBT is an appropriate treatment option.
Dialectical Philosophy in DBT
The dialectical philosophy is a fundamental principle of Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT). It emphasizes the balance and integration of seemingly opposing concepts, such as acceptance and change. This approach encourages individuals to accept their current thoughts, emotions, and circumstances while simultaneously working towards positive change and personal growth.
The term “dialectical” refers to the process of reconciling contradictions or finding a synthesis between two opposites. In DBT, this often involves recognizing that multiple perspectives can coexist and that truth can be found in the integration of these differing viewpoints. The dialectical philosophy helps clients develop a more balanced and flexible mindset, which can be crucial in overcoming rigid thought patterns and ineffective coping strategies.
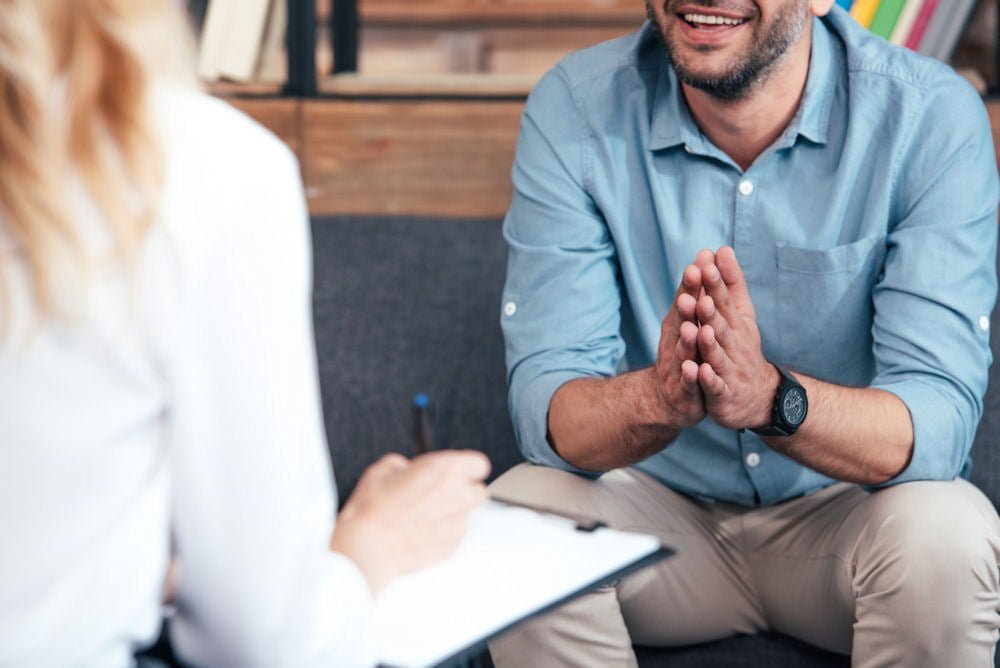


The Core Elements of a
Dialectical Behavior Therapy Program
Despite the various forms of DBT available, certain primary features remain consistent across most versions of the therapy. At Bayview Recovery, our DBT treatment program incorporates these core elements to provide comprehensive and effective care for our clients.
Individual therapy is a crucial component of any DBT program. During these one-on-one sessions, which typically occur once a week, the therapist works closely with the client to enhance their motivation, develop coping skills, and apply the learned techniques to real-life situations. By addressing the specific needs and challenges of each individual, this tailored approach helps clients make meaningful progress in their recovery journey.
Skills training sessions are another essential aspect of DBT. These classes, which also take place about once a week, aim to teach clients various practical skills that can help them navigate everyday challenges more effectively. Some of the key areas addressed in skills training include mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. By participating in these sessions, clients can develop a greater sense of self-efficacy, empowering them to make healthier choices and maintain long-term recovery.
Skills training sessions are another essential aspect of DBT. These classes, which also take place about once a week, aim to teach clients various practical skills that can help them navigate everyday challenges more effectively. Some of the key areas addressed in skills training include mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness. By participating in these sessions, clients can develop a greater sense of self-efficacy, empowering them to make healthier choices and maintain long-term recovery.
Acceptance and mindfulness are central components of DBT, playing a significant role in fostering emotional regulation and personal growth.
Acceptance: In DBT, acceptance refers to the non-judgmental acknowledgment of one’s current thoughts, emotions, and experiences. By practicing acceptance, clients learn to recognize and validate their feelings without becoming overwhelmed or resorting to unhealthy coping mechanisms. Acceptance does not imply resignation or passivity; instead, it serves as a starting point for change and growth. By embracing acceptance, clients can develop self-compassion and cultivate a more adaptive response to life’s challenges.
Mindfulness: Mindfulness is the practice of maintaining a non-judgmental awareness of the present moment. It involves paying attention to one’s thoughts, emotions, and bodily sensations without getting caught up in judgments or evaluations. In DBT, mindfulness practices are incorporated into skills training sessions to help clients develop greater self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Mindfulness helps clients observe their internal experiences objectively, allowing them to recognize unhelpful thought patterns and emotional reactions. By cultivating mindfulness, clients can develop a greater sense of control over their thoughts and emotions, leading to more effective decision-making and healthier coping strategies.
The primary features of a dialectical behavior therapy program at Bayview Recovery are designed to offer a comprehensive and personalized approach to addiction treatment. The dialectical philosophy in DBT emphasizes the balance between acceptance and change, fostering a more flexible and adaptive mindset. By incorporating individual therapy, skills training, therapist consultation, acceptance, and mindfulness, our DBT program helps clients develop the motivation, skills, and support needed to overcome the challenges of addiction and achieve lasting recovery.
What are the Five Functions of
Treatment Using DBT?
The five functions of treatment using Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are designed to address various aspects of an individual’s well-being and recovery. These functions ensure a comprehensive approach to therapy, focusing on building personal skills, enhancing motivation, and providing support. The five primary functions of DBT treatment are.
This function aims to teach new skills that enable individuals to manage their emotions, cope with stress, improve interpersonal relationships, and engage in healthier behaviors. Skills training sessions focus on areas such as mindfulness, emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness.
DBT addresses any ambivalence or resistance towards change by fostering motivation to engage in healthier behaviors and maintain recovery. Individual therapy sessions often focus on identifying personal values, setting achievable goals, and reinforcing commitment to change.
To promote lasting change, DBT emphasizes the importance of applying newly learned skills to real-world situations. Therapists help clients identify opportunities for skill practice outside of therapy sessions and provide support and guidance to ensure the successful implementation of these skills in everyday life.
DBT recognizes the impact of an individual’s environment on their recovery. This function focuses on creating a supportive and structured treatment environment that facilitates growth, healing, and progress. This may involve modifying aspects of the client’s living situation, social circle, or daily routine to minimize triggers and enable the successful application of newly acquired skills.
To ensure the highest quality of care, DBT therapists participate in regular consultation meetings with their peers. These meetings allow therapists to discuss client progress, share insights, address challenges, and receive feedback on their therapeutic approach. This ongoing collaboration and support help therapists continuously improve their skills and stay motivated in their work.
The five functions of treatment using DBT provide a comprehensive and effective approach to addressing the complex needs of individuals struggling with mental health and behavioral issues. By focusing on enhancing capabilities, improving motivation, ensuring generalization, structuring the environment, and enhancing therapist capabilities, DBT helps build a well-rounded approach to addiction treatment and mental illness.


Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Center at Bayview Recovery
If you or a loved one has a problem with addiction, then dialectical behavior therapy can be a powerful tool to help you and them control one of the primary drivers of this deadly illness. You can participate in a dialectical behavior therapy program as well as a host of other leading and proven treatments for drug and alcohol abuse at Bayview Recovery. Our treatment modalities include:
Individual, group, and family therapy
Holistic therapies
Somatic and trauma therapy
All our programs are led by highly-qualified counselors who have direct experience treating addiction, and you can have your treatment in a facility designed for maximum comfort so you can focus on healing. Call Bayview Recovery today to learn more and start getting well.
“The staff at the center has been remarkable in their care for our loved one. Tuni was with us the whole way as we tried to get this person into treatment. They continue to assist us as the process continues. Great work!”
Ray O
“I have been trying to get sober the past 3 years and I have been to treatment 5 times. Bayview Recovery was my 6th time. They helped me get to 142 days sober! I was a handful hot mess when I got there but the team never gave up on me. They work with families and they truly care about them too. Bayview house’s are clean and comfortable and the staff is amazing. They plan for fun events weekly and they want you to have fun. If your looking for something different call them it will save your LIFE!”
Cindy J
“Bayview is dedicated to providing clients the healthiest environment to develop a solid foundation in their recovery. The therapists and medical team are devoted to ensure clients have the best individualized care. I highly recommend Bayview for anyone seeking a highly professional treatment program. The care and compassion given to clients is remarkable.”
Robin M
“This is a fantastic facility with outstanding staff. If you or a loved one is struggling this is a great program to start the journey of recovery and get life long skills and relationships to begin a new life!”
Garrett T
“Just picked up our daughter after 90 days at Bayview Recovery. Loved the staff and facility, do not know what the future holds ???????? but while at Bayview , always felt informed. Highly recommend, incredibly helpful especially at the very beginning when we were so helpless and needed help the most – God Bless.”
Rosie S
Dave Cundiff, MD, MPH is an experienced leader in the field of Substance Use Disorder treatment. He works with patients suffering from Substance Use Disorder to evaluate their medication needs and prescribe treatments accordingly. In addition, he regularly participates in all-staff debriefing sessions involving peers, nurses, and other prescribers. He also reviews and advises on policies, procedures, and techniques for treating substance use disorder.